MAKE AN APPOINTMENT TODAY!
Shoulder Arthritis
|
The shoulder is composed of the acromioclavicular and the glenohumeral joints. The acromioclavicular joint is formed by a junction between the collarbone (clavicle) and the tip of the shoulder bone (acromion). The glenohumeral joint is formed by an articulation of the upper arm bone (humerus) with the shoulder blade (scapula). The three major types of shoulder arthritis are osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and post-traumatic arthritis.
Osteoarthritis affects the cushioning cartilage on the ends of shoulder bones that enables them to move smoothly. Osteoarthritis occurs when the cartilage is damaged as a result of previous injury to the shoulder, or normal wear and tear process as we age. As the cartilage is destroyed, the bones begin to rub against each other and cause pain, stiffness and weakness. Rheumatoid arthritis causes joint lining (synovium) swelling and joint space narrowing. It progressively destroys the bones and soft tissues of both shoulders and other joints of the body. Post-traumatic arthritis is a form of osteoarthritis that develops after an injury, such as a shoulder fracture, dislocation, or a rotator cuff tear. |
Arthritis Symptoms
Patients with shoulder osteoarthritis usually complain of progressively worsening pain, which is aggravated by normal daily activities. In the glenohumeral joint OA, the pain is often felt in the back of the shoulder while in the acromioclavicula joint osteoarthritis, the pain is centered on the front of the shoulder.
Pain in both shoulders and other joints in the body is a sign of rheumatoid arthritis. In the early stages of rheumatoid arthritis, only one shoulder joint may be affected. Swelling of the shoulder is more common with rheumatoid arthritis .
In both, rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis, patients often experience decreased shoulder range of motion, which makes it difficult, for example, to comb hair or reach for items on high shelves. Pain is commonly accompanied by clicking or snapping sound with shoulder movement. Night pain is common in the advanced stages of shoulder arthritis.
Pain in both shoulders and other joints in the body is a sign of rheumatoid arthritis. In the early stages of rheumatoid arthritis, only one shoulder joint may be affected. Swelling of the shoulder is more common with rheumatoid arthritis .
In both, rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis, patients often experience decreased shoulder range of motion, which makes it difficult, for example, to comb hair or reach for items on high shelves. Pain is commonly accompanied by clicking or snapping sound with shoulder movement. Night pain is common in the advanced stages of shoulder arthritis.
Arthritis Diagnosis
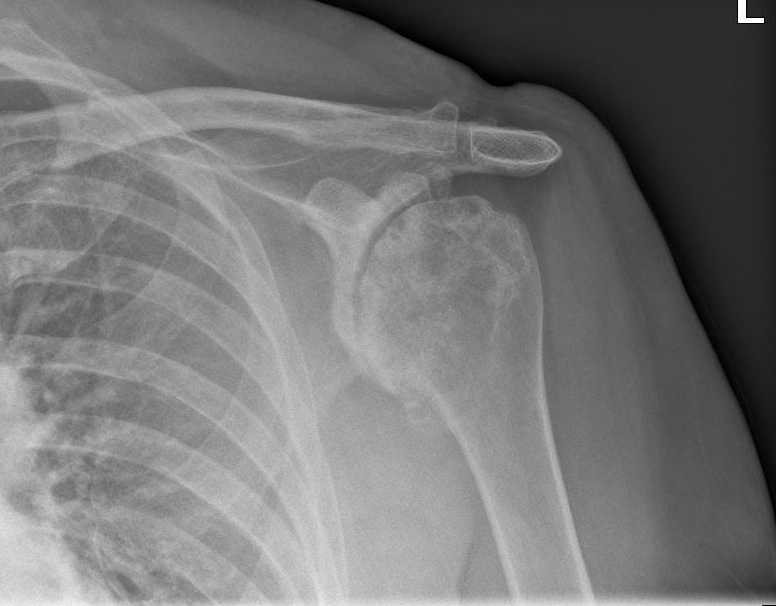
A detailed history including medical conditions, activities that aggravate shoulder use, and any prior injuries is important. During a physical examination, your doctor will look for tenderness and swelling, limited range of motion as well as identify positions which cause pain to your shoulder joints. X-ray will be taken to evaluate the extent of joint damage and to check for any evidence of fractures. By the time shoulder arthritis can be seen on x-rays, there has been significant damage to the shoulder joints’ surfaces.
Arthritis Treatment
Treatment options depend on the severity of shoulder arthritis symptoms and the patient’s overall medical health.
Nonsurgical TreatmentNon-surgical treatment options include pain control, physical therapy, heat and cold therapy, and corticosteroid injections.
Surgical TreatmentSurgical treatment is recommended when the conservative, non-surgical intervention fails to adequately control patient’s symptoms.
|
Disclaimer and Privacy
IZADIHAND.COM © 2011-2022 Kayvon David Izadi MD - All Rights Reserved
Webmaster
IZADIHAND.COM © 2011-2022 Kayvon David Izadi MD - All Rights Reserved
Webmaster