MAKE AN APPOINTMENT TODAY!
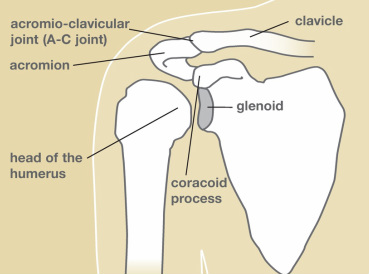
Shoulder FracturesThe shoulder joint is suspended by many muscles surrounding the upper extremity. The shoulder bones include the clavicle (collarbone), the scapula (shoulder blade), and the humerus (upper arm bone), see Figure 1. The only connection of the shoulder girdle to the remainder of the skeleton is the clavicle. The scapula is an important part of the shoulder joint as it serves as an anchor for many muscles and contains the socket part of the shoulder (glenoid). The upper end of the humerus has a ball-like shape that articulates with the socket, and the humerus also serves as an attachment point for many muscles and tendons. One of the most important is the rotator cuff. Disruption of any of these parts can create difficulty with the function of the shoulder.
Shoulder Fracture TypesShoulder fractures vary by age. The majority of shoulder fractures in children occur in the clavicle. In the adult, shoulder fractures within the upper part of the arm (proximal humerus) occur with increasing frequency with older age. Some shoulder fractures may occur with dislocation of the shoulder joint.
|
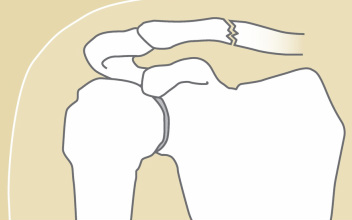
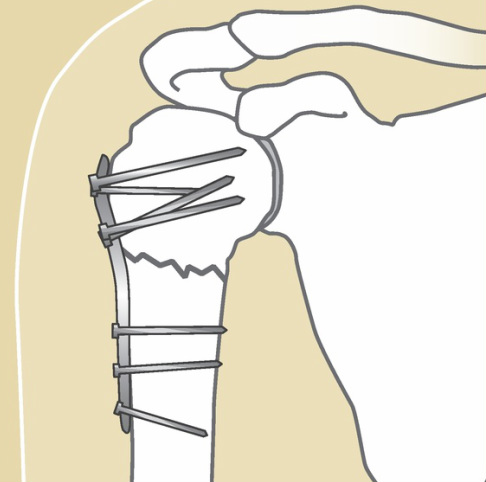
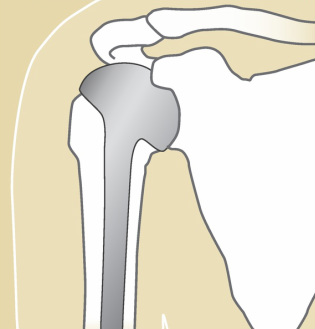
Clavicle FractureThe most common shoulder fracture is of the clavicle, frequently the result of a fall onto the shoulder (see Figure 2). These fractures can be quite painful and cause difficulty in moving the arm. Classically, treatment has been non-operative. Treatment can be a simple sling or a “figure 8” strap, worn for three to eight weeks, depending on one’s pain. Once healed, there may be a bump over the fracture site which may decrease with time, but sometimes a deformity may remain permanently. Range of motion can begin as soon as pain subsides; return to sports cannot occur until full shoulder strength returns. Return to contact sports would be considered only when the shoulder fracture is fully healed on X-ray. Recently, surgical treatment of these fractures has been reconsidered. Surgical treatment options may include plates and screws or even a rod placed into the bone. The consideration of these treatment options depends upon one’s activity level and the dominance of arm use, i.e. a right-handed athlete with injury to the right clavicle versus an older individual not engaged in “overhead” activities.
|
|
|
Reproduced with permission from the American Society for Surgery of the Hand www.handcare.org
Disclaimer and Privacy
IZADIHAND.COM © 2011-2022 Kayvon David Izadi MD - All Rights Reserved
Webmaster
IZADIHAND.COM © 2011-2022 Kayvon David Izadi MD - All Rights Reserved
Webmaster